AS/NZS 4308 Cut-off Levels: What Are These?
24 September, 2023

AS/NZS 4308 is the Australian and New Zealand Standards for urine drug testing in the workplace. It provides guidelines and procedures for collecting and testing urine samples to detect the presence of illegal drugs or prescription medications. One key aspect of this testing is the establishment of AS/NZS 4308 cut-off levels. These are minimum concentrations of a drug or its metabolites that must be present in a sample to be considered positive.
Urine screening is a widely used method of drug testing for workplace compliance or medical purposes. It is easy to administer and provides accurate results. In addition, it can detect a wide range of substances for an extended period. Thus, it is vital to use reliable methods to ensure the validity and integrity of the test. In this article, we will delve into the details of AS/NZS 4308, particularly the cut-off thresholds and their purpose for workplace testing.
AS/NZS 4308 Cut-off Levels: Urine Immunoassay Screening
Urine immunoassay screening is a type of test that uses immunoassay or antibodies to detect specific substances in a sample. This method can provide valuable information about a person’s consumption of drugs. Through this test, health professionals can diagnose potential substance abuse and other medical conditions. The AS/NZS 4308 cut-off levels are specific thresholds for each drug class.
The cut-off levels of drugs in urine are expressed in nanograms (ng) per millilitre (mL). The initial cut-off will also vary with confirmation levels. The common drugs of abuse and the minimum levels for confirmation in urine are amphetamines – 250ng/mL, MDMA – 250ng/mL, cocaine metabolites – 300ng/mL, marijuana or cannabis metabolites – 50ng/mL, and phencyclidine (PCP) – 25ng/mL
Workplaces use urine drug screening because it is cost-efficient and less invasive than blood tests. It involves collecting a pre-established amount and analysing it using rapid testing kits or equipment. Thus, it gives instant results in as fast as five minutes. If the test shows non-negative results, it requires confirmatory testing through advanced laboratory techniques to validate the results.
Laboratory Cut-off Levels for Confirmation
The cut-off thresholds for confirmation or laboratory testing in urine are considerably lower than immunoassay screening. This is a more sensitive test than point-of-care tests (POCTs) to identify compounds correctly. The following are the cut-offs for laboratories:
- Amphetamine-type substances – 150ng/mL
- Cocaine metabolites – 150ng/mL
- Marijuana or cannabis metabolites – 15ng/mL
- Codeine – 300ng/mL
- Morphine – 300ng/mL
- 6-Acetylmorphine – 10ng/mL
Important points:
- Confirmation testing uses Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) techniques, which are referred to as the gold standard in drug testing.
- Laboratories make allowance for the cut-off amount of cannabis for passive smoking.
- Uncertified testing kits may have different cut-off thresholds.

AS/NZS 4308 Cut-off Levels: Oral Fluid Immunoassay Screening
Apart from AS/NZS 4308 cut-off levels, another testing method that employers use is AS/NZS 4760 for oral fluid testing. This immunoassay screening detects drugs in a person’s saliva. The process involves swabbing the inside of the cheek with an absorbent stick and testing it against specific antibodies. Saliva samples can trace substances within 5 to 48 hours after consumption.
One reason why oral fluid screening is beneficial is its non-invasive nature. Collecting a saliva specimen is relatively easy and has no privacy issues. Furthermore, it can provide a more accurate representation of an individual’s current drug use compared to urine or hair tests. This is because substances are quickly absorbed into the bloodstream and into salivary glands after ingestion.
The oral fluid testing process is a convenient option, giving the results within a short period of time. Thus, it is reliable for monitoring drug use in real time and identifying individuals who may be under the influence. The drug screening cut-offs for oral fluids are as follows: amphetamine substances – 50ng/mL, cannabis metabolites – 15ng/mL, cocaine metabolites – 50ng/mL, opiates – 50ng/mL, and oxycodone 40ng/mL.
Laboratory Cut-off Levels for Confirmation
The new laboratory cut-off thresholds for saliva drug testing include changes to marijuana and the addition of oxycodone. THC (marijuana/cannabis) has a lower cut-off at 5ng/mL from 10 ng/mL. Oxycodone, a strong painkiller, became mandatory with a cut-off of 20ng/mL. These changes were included in the chain of custody documents of 2019.
Other substances include opiates – 25ng/mL, amphetamine – 25ng/mL, and cocaine 25ng/mL). A test is positive if a person’s sample has reached any of these amounts. The results are final, which employers can form as a basis for decision-making. Employees may face the corresponding consequences depending on the workplace policy.
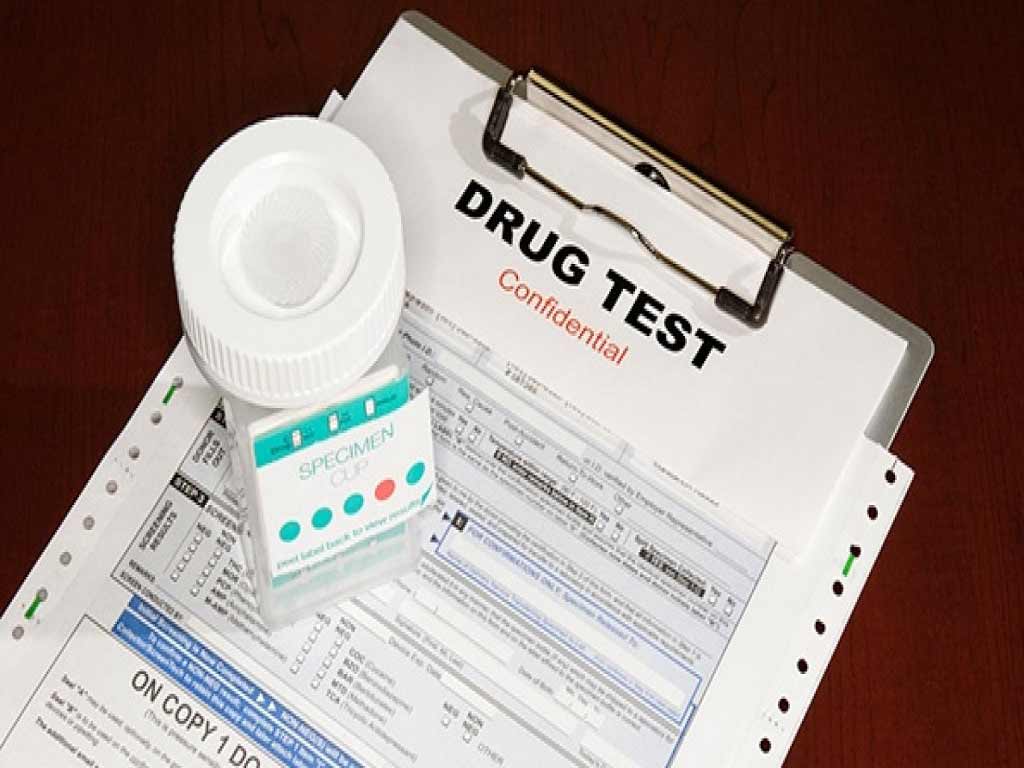
AS/NZS 4308 Cut-off Levels: Purpose
The purpose of AS/NZS 4308 cut-off levels is to establish guidelines for the interpretation of drug test results in the workplace. These thresholds determine the concentration of substances in a person’s system. By setting the minimum requirements, it ensures the results are reliable and reduces the chance of false positives.
Another purpose of these standards is for health professionals and employers to determine if drug usage has reached a hazardous level. Moreover, the test involves specific steps on how to collect, transport, store, and analyse urine specimens. This chain of custody process ensures that the sample is valid and follows hygienic measures. Furthermore, it protects employers from potential wrongful or negligent termination claims if an employee fails a drug test.
Organisations conduct drug and alcohol testing for various circumstances. The common reasons are to screen job applicants, determine the cause of an accident, and test a suspicious employee. In addition, random testing is a standard practice in high-risk industries. Employers administer this test to monitor impairment in workers at any given time.
Effects of Abusing Illegal Substances
The abuse of illicit drugs can have a multitude of negative effects on both the individual and society. Firstly, substance abuse can harm or damage the vital organs, such as the liver, heart, and brain. Long-term abuse can also lead to mental health issues like depression, anxiety, and psychosis.
Moreover, substance abuse or addiction can affect a person’s productivity and performance at work. This can lead to an increase in workplace accidents, absenteeism, and tardiness. It is also often linked to violence and crimes. Finally, it can place a significant burden on healthcare systems, as individuals may require medical treatment or rehabilitation.
Conclusion
AS/NZS 4308 cut-off levels are important standards for drug testing in the workplace. The purpose of these standards is to provide reliable results and protect employers from potential wrongful or negligent termination claims. Different drug classes have different thresholds, with laboratory confirmatory testing having lower levels to ensure accuracy and precision. Furthermore, the cut-offs for urine are different for oral fluids. Thus, it is vital for employers to choose the appropriate methods depending on the situation.
Employers conduct workplace testing to minimise drug-related hazards, including accidents, violence, and low productivity. It also aims to deter potential abuse that can affect others. A set standard enhances the accuracy of the test and ensures that it is consistent with national and healthcare guidelines. Moreover, it helps protect companies from legal issues. Overall, drug tests are a vital tool to ensure a safe and healthy workplace.