Drug & Alcohol Test: The Need to Know
10 January, 2024

Substance abuse is a widespread problem that can lead to hazardous behaviour and safety risks. It affects not only the individual but also the community. Hence, the need for drug & alcohol tests increases to combat the hazards of illicit substances. This measure involves the collection and analysis of biological specimens to detect the presence of alcohol and drugs. The results of the test can determine if a person is impaired during an incident or if they have addiction problems.
Testing for drugs and alcohol is a common practice in many settings, particularly in law enforcement, healthcare, and workplaces. It is a sensitive procedure that requires care and caution when being implemented. It is also vital to understand how it works and what are the options available. This article will explore the processes of testing, the types of methods, and the consequences of positive results.
Overview of Drug & Alcohol Testing
Drug & alcohol testing is an examination of body samples to check for consumption or exposure to specific substances within a period of time. The tests utilise various techniques of detection and measurement with varying levels of accuracy and sensitivity. A common analytical technology is Immunoassay (IA) screening, which can trace substances rapidly.
The IA test is simple, cost-efficient, and easy to administer. It is also relatively inexpensive, making it the preferred option of most employers for preliminary or onsite screening. Another type is Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS). It involves laboratory analysis and can provide more detailed and accurate information. GC-MS test is often used for confirmation of an initial non-negative result.
This testing is crucial in various settings to ensure safety, prevent accidents, and promote overall well-being. In the workplace, it can help screen prospective employees to ensure the new hires do not have risky or abusive behaviours. Additionally, it is valuable in determining if alcohol or illicit drugs are a factor in an accident.
Reasons for Testing
- Workplace safety: Testing helps to identify individuals who may be impaired and at risk of causing accidents or making mistakes at work.
- Legal compliance: Many industries follow regulatory drug and alcohol screening to maintain safety standards.
- Substance abuse prevention: Regular testing can act as a deterrent for employees to engage in drug and alcohol consumption, promoting a healthier lifestyle.
- Enhance productivity: Workplaces maintain a stable workforce, leading to high job performance. Testing discourages employees from coming to work under the influence, reducing instances of absenteeism or tardiness.
- Monitor treatment: It helps health professionals track the recovery of patients.
Types of Drug & Alcohol Tests
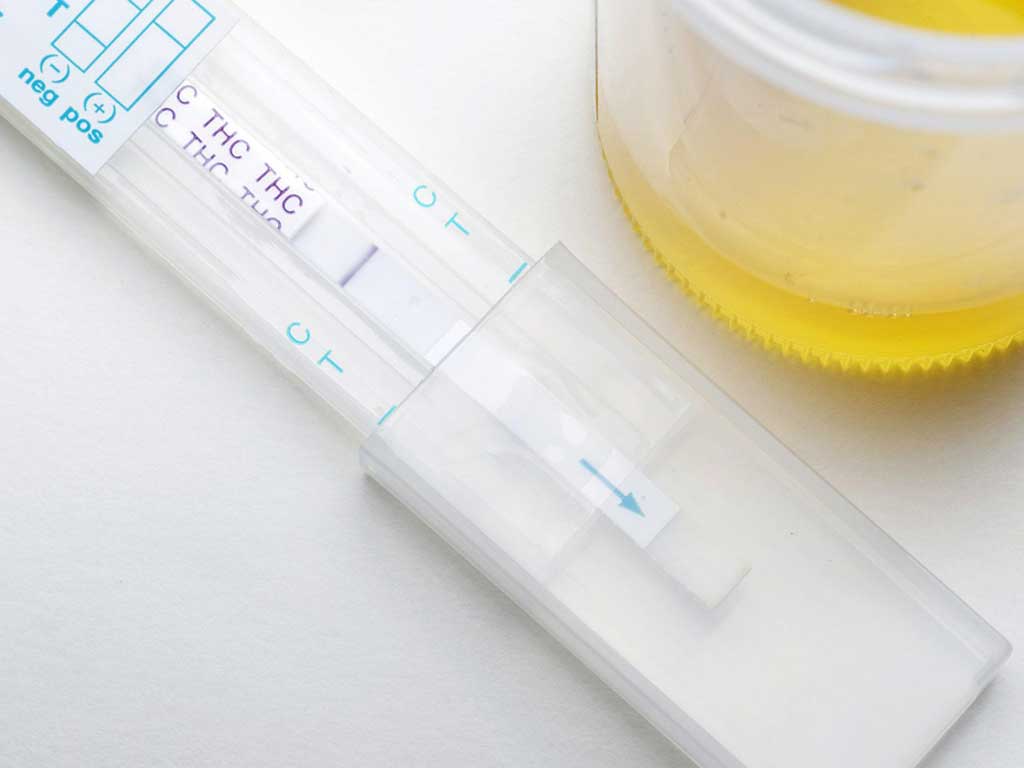
Drug & alcohol tests come in various types, each with its own advantages and limitations. The choice of test depends on various factors, including the purpose of testing, the desired level of accuracy, and the availability of resources. One of the most common types of drug tests is urine testing. This method is easy to administer and can provide results within a few hours or days.
The second type is the blood test, which can detect the presence of drugs and alcohol in the system. They are typically more accurate than urine tests, as they can provide real-time information about the substance use of a person. However, they are generally more invasive and require special collection facilities and licensed professionals to administer them.
Another type is saliva testing. It is a popular choice for random drug screening and is less invasive than urine and blood tests. They are standard practices in roadside sobriety checkpoints to determine if a person is under the influence of drugs while driving. Lastly, the breath test can measure Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) levels of a person.
Substances that Can Be Detected
Drug screening services can detect a wide range of drug classes or drug metabolites. This includes illegal drugs that can pose serious health and safety risks. In particular, the tests can identify amphetamine substances, such as marijuana, heroin, and cocaine, that people use as recreational drugs.
Organisations may also test for prescription drugs, which can indicate unsanctioned use. The most abused prescribed medications include opioids and benzodiazepines. Furthermore, alcohol testing services look for traces of ethanol or its biomarkers like Ethyl Glucuronide (EtG) and Ethyl Sulfate (EtS). However, the presence of EtG and EtS does not mean impairment at the time of the test.
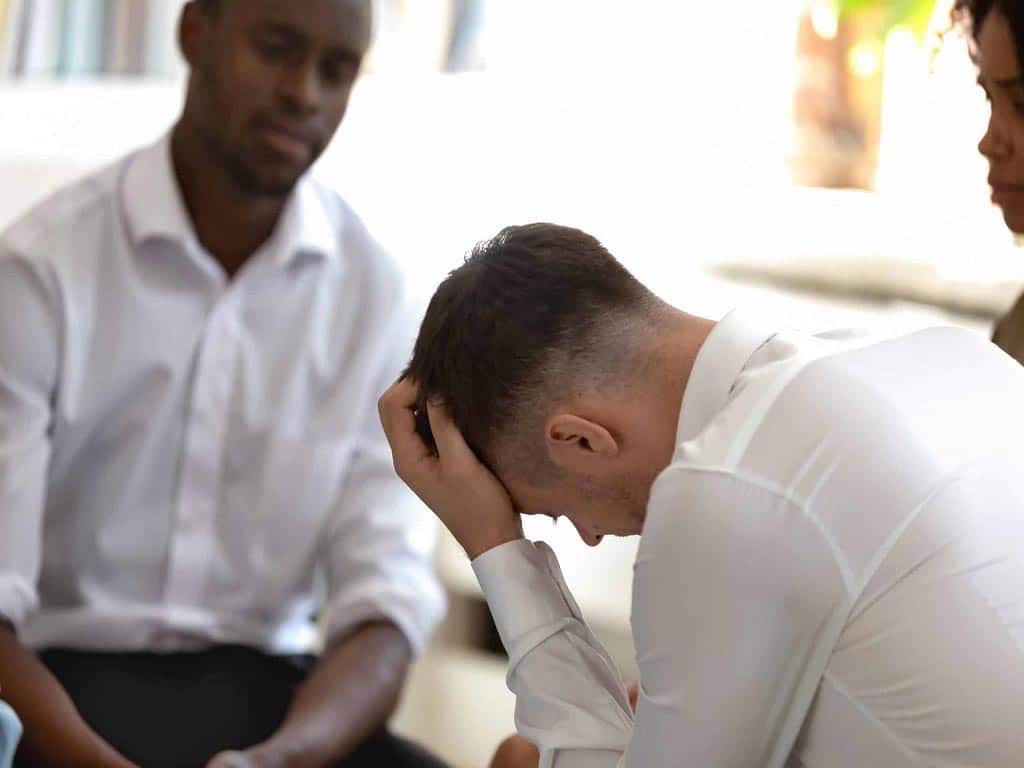

Implications of a Positive Drug & Alcohol Test
A positive drug & alcohol test results can have several implications, especially in employment or legal situations. In workplace drug testing, a positive test can result in suspension or even immediate termination. The consequences may depend on the alcohol and drug policy of a company. Nevertheless, it is important for companies to follow the protocols in serving disciplinary actions to ensure fairness and consistency.
In legal situations, a positive test can have serious penalties. It can serve as evidence in indictable offences, such as Driving Under the Influence (DUI). These legal consequences can have long-lasting effects on personal and professional life, including imprisonment, difficulties in obtaining insurance coverage, loss of driving privileges, and limitations in career opportunities.
Moreover, it can impact child custody hearings or probation requirements for individuals on parole or probation. For example, it can affect the visitation rights of a parent. Lastly, a failed test result may lead to mandatory substance abuse treatment. This is often mandatory for individuals who are found to have an addiction problem to help them on their path to recovery.
Treatment Programs and Resources
One common treatment program is outpatient rehabilitation. This type of program allows individuals to receive treatment while still living at home. It typically involves regular counselling sessions and support groups, as well as medication-assisted treatment if necessary. Outpatient programs are often more affordable and flexible, allowing individuals to maintain their daily responsibilities while receiving the help they need.
Inpatient rehabilitation involves staying at a treatment facility for a designated period. This type provides a structured and supportive environment where individuals can focus solely on their recovery. It is beneficial for people with severe addiction or those who require a higher level of care and support.
Conclusion
Drug & alcohol testing is an important tool for detecting the presence of prohibited substances in a person. It is valuable in high-risk workplace settings, legal situations, and rehabilitation programs to ensure safety and effective recovery. Additionally, there are several types of alcohol and drug testing procedures that are suitable for different situations. The common methods are urine, saliva, blood, and breath testing. Each type provides distinct advantages and limitations.
Moreover, the test can detect a wide range of drug classes that can affect the physical and mental abilities of a person. Therefore, regular screening is crucial to ensure the safety of employees and deter substance abuse. Lastly, positive confirmatory testing can have significant implications, such as job loss or legal penalties. Therefore, resources for treatment should be readily available to help affected individuals regain control of their lives and overcome addiction.