Ethanol Identification Test: Definition, Methods, & The Process
20 March, 2024

Ethanol, or ethyl alcohol, is a common ingredient in alcoholic beverages, fuel, and household products. It is essential to accurately identify and test ethanol to determine its purity and concentration. An ethanol identification test is a screening method. Typically, professionals conduct it in a medical facility. They utilise various methods, such as chromic acid solution and distillation process. Moreover, they can analyse a sample of breath using a breathalyser. The process usually involves chemicals that react with ethanol.
Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to various health problems, including liver damage, impaired judgment, and addiction. Additionally, ethanol poisoning is a serious concern, as it can result in respiratory failure, coma, and death. As such, the precise screening of ethanol is crucial for ensuring the safety and well-being of individuals. The article will present this type of medical testing, the screening methods, and the different processes medical practitioners use to test ethanol.
What is an Ethanol Identification Test?
An ethanol identification test is a commonly used method to determine the presence of alcohol, specifically ethyl alcohol, in various substances. Generally, chemical analysts, medical providers, and law enforcement officials perform the test in laboratory settings to ensure the accuracy and safety of products. They also test ethanol to determine the Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) of subjects.
Identifying the concentrations of ethanol can help determine if a substance is safe for consumption or use. For example, in the food and beverage industry, ethanol tests are crucial to ensure that products meet regulatory standards for alcohol content. In medical settings, these tests are used to monitor patients who may be at risk of alcohol poisoning or other interactions.
Businesses and organisations can avail of ethanol testing services from third-party laboratories. Also, they can buy testing kits or devices. In addition, companies can train their staff to perform the test in-house. Businesses can maintain product quality and safety standards by ascertaining precise results. Ultimately, this builds trust with consumers and regulatory bodies.
Importance of Identifying Ethanol in Various Substances
- Detecting ethanol in various substances is essential for safety reasons. Ethanol is highly flammable. Its presence in certain substances could pose a fire hazard. Knowing whether or not ethanol is present allows for appropriate precautions to be taken.
- Alcohol consumption can have detrimental health effects. These include addiction, liver damage, and impaired judgment. Identifying ethanol in substances, such as beverages or medications, enables individuals to make informed decisions.
- Various industries, like pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and fuel, use ethanol. Identifying ethanol in these substances is vital to ensuring quality control. Accurate measurement of ethanol concentration can help prevent product contamination and maintain product consistency.

Methods for Ethanol Identification Test
One method for ethanol identification test is the use of chromic acid reagent. In this test, professionals mix a few drops of the substance to be tested with the reagent. Subsequently, this results in a colour change from orange to green if ethanol is present. This reaction mixture occurs due to the oxidation of ethanol by chromic acid.
Another method is the distillation process. In this method, practitioners heat the substance in question. Then, they collect and condense the ethanol vapour into liquid form. Afterwards, they test the resultant liquid for the presence of ethanol using various techniques, such as gas chromatography or infrared spectroscopy. Analysing the characteristic peaks or absorption bands allows the accurate determination of the presence and concentration of ethanol.
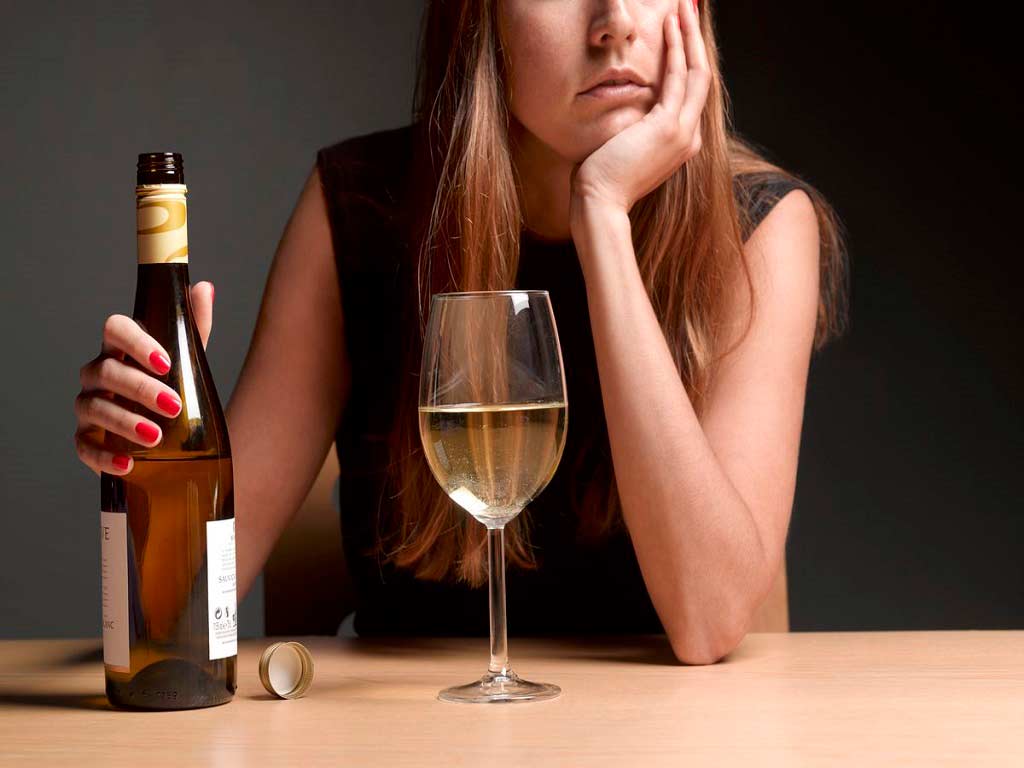
A common alcohol identification test is through breathalysers. This non-invasive technique detects alcohol consumption and measures alcohol concentration in the breath through exhaled air. The tester utilises a fuel cell or an infrared sensor. It presents the result as blood alcohol content percentage. Breath testing is beneficial because it can provide instant outcomes, unlike other methods that detect ethanol. These include collecting blood samples.
Techniques for Identifying Ethanol
Professionals employ various techniques to identify the presence of alcohol. One of these is Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS). It is a sensitive and accurate method. The test separates the components of a mixture based on their vapour pressure and affinity to the stationary phase. Comparing the retention time of the sample with standard compounds determines ethanol concentration.
In addition, there is Infrared Spectroscopy (IR). This technique measures the absorption of infrared light by the sample, allowing for the identification of specific functional groups present in the molecule. Ethanol exhibits unique infrared absorption bands, aiding in its identification and differentiation from other compounds.

Process for Ethanol Identification Test
The ethanol identification test process involves a series of steps to determine the presence and concentration of ethanol in a given sample. Firstly, professionals mix the specimen with an oxidising agent. Then, this oxidises the ethanol to acetic acid. It turns the orange solution green in the presence of sulfuric acid. This colour change indicates the presence of ethanol.
Once the initial test confirms the presence of ethanol, the sample is subjected to distillation. Distillation helps separate the ethanol from the sample by boiling the mixture and collecting the vapour. Afterwards, practitioners confirm its identity and purity. It is through a confirmatory test such as the Lucas test. Providers mix ethanol with hydrochloric acid and zinc chloride. If a cloudy white layer forms, it indicates the presence of ethanol.
The process of detecting blood alcohol concentration through a breathalyser is simpler. It measures the amount of ethanol in the breath, which correlates directly to the amount in the blood. Testing happens through a chemical reaction that produces an electrical current proportional to the concentration of alcohol. This type of medical testing can help prevent excess alcohol intake.
Factors that Can Influence Ethanol Detection
Various factors can influence ethanol detection. These include the type of sensor. Different sensors will have varying levels of responsiveness to ethanol, which can affect the reliability of the identification. Additionally, external factors can impact ethanol detection. For instance, higher temperatures can cause ethanol to evaporate more quickly, leading to easy identification.
Furthermore, the type and amount of alcohol a person consumes can affect the accuracy of the test. Different types of alcoholic beverages contain varying levels of ethanol, so the sensor must be calibrated accordingly. Meanwhile, the higher the consumption, the more ethanol will be present in the breath, making it easier to identify.
Conclusion
The ethanol identification test is a reliable and efficient method for determining the presence of ethanol in a given sample. This test uses qualitative and quantitative methods to analyse the composition of a liquid and ascertain the presence and concentration of ethanol. For example, professionals may utilise chromic acid and distillation process. Moreover, they can do ethanol testing through breathalysers. It is more reliable than collecting blood or urine samples because it provides immediate results without invasive procedures.
The ethanol test typically involves a series of steps. First, professionals mix the sample with a reagent. Then, the reagent reacts with ethanol to produce a colour change. Afterwards, they can compare this colour change to a known standard to determine the presence and concentration of ethanol in the sample. Additional testing is done after the procedure. Breathalyser tests also use a chemical reaction to detect ethanol in the breath and measure the blood alcohol content.