DAS Screen: Definition & the Testing Procedures
01 April, 2024
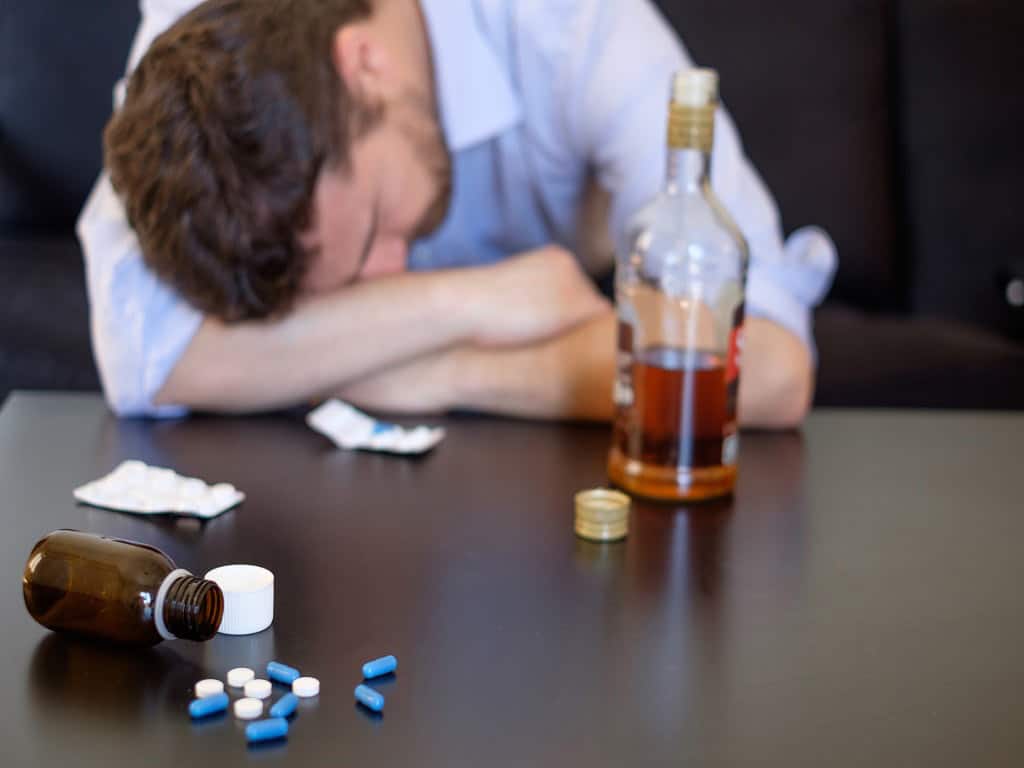

Drug and Alcohol Screening (DAS) refers to the process of testing individuals for the presence of drugs or alcohol in their system. There are various methods to screen for substance use, such as urine, saliva, and breath testing. In addition, the implementation of DAS screening is prominent in roadside screenings, workplaces, rehabilitation centres, and legal settings. Thus, it helps to manage safety risks brought about by substance impairment.
Heavy alcohol consumption, prescription drug abuse, and illegal drug usage have detrimental effects, such as liver damage, heart problems, and an increased risk of accidents and injuries. Additionally, they impair judgment, coordination, and cognitive function, leading to poor decision-making and risky behaviours. Consequently, individuals, professionals, and authorities rely on drug and alcohol screening. This article will provide information on drug and alcohol screening, including the different types of procedures and how to understand the results.
What is DAS Screening?
DAS screening is a standard process used in various settings. It involves collecting and analysing biological samples to detect illegal drugs or alcohol biomarkers. The presence of these substances can indicate recent use or impairment. It can also provide valuable information if a person has a substance use disorder and needs further evaluation.
The screening process typically uses portable drug test kits, which can yield rapid results. Additionally, these testing devices utilise immunoassay to detect drug compounds quickly. The immunoassay technique involves the use of antibodies that produce a visible chemical reaction when they interact with specified substances in the sample. The test can indicate a positive and non-negative result within seconds, allowing individuals, employers, or officers to make immediate decisions.
People can avail of drug and alcohol screening services from various providers. These include the closest collection centre, medical clinic, laboratory, or specialised testing facility. Additionally, they can purchase alcohol testing devices or drug test kits for convenience. Nevertheless, they must remember the accuracy and reliability of the test results can vary depending on the expertise of the provider and the testing method.
Importance of the Screening
- In the workplace, screening for alcohol and illicit drugs helps identify employees who are impaired while working. This helps reduce the risk of accidents and injuries.
- Identify individuals who may have alcohol and drug abuse and offer intervention or connect them with resources for treatment.
- In primary care settings, alcohol and drug screening can help health professionals identify patients who may be at risk due to substance abuse.
- In road settings, screening can determine if individuals are under the influence of substances while driving.
- In probation, screening for drugs and alcohol can ensure compliance with court-mandated sobriety requirements.

Types of DAS Screening Procedures
Different types of DAS screening procedures are advantageous in diverse situations. The most common type is urine screening. This method is widely used due to its ease of sample collection and has an average of 48-window period of detection. Furthermore, the test kits include a small container cup and a test strip or cassette to analyse the sample from the point of collection.
Saliva drug screening is another popular method for testing. It is used in roadside inspections because the saliva sample collection procedure is non-invasive and can be done under the supervision of a police officer. Many workplaces also use saliva tests to determine recent drug use. It has a detection window of up to 24 hours.
An efficient method of detecting alcohol intoxication is breath alcohol testing. It uses a breathalyser device. The machine can measure the alcohol concentration levels in the system through the breath sample. The test is also non-invasive and can display the results on the screen within 10-15 seconds.
Commonly Tested Substances
Drug and alcohol screening can detect a wide range of substances, including illegal drugs and prescription medications. It usually tests for marijuana, cocaine, heroin, ecstasy, and methamphetamine. In addition, prescription drugs are detectable, including opiates, opioids, amphetamines, and benzodiazepines. These substances have different periods of detection in different types of tests.
Furthermore, alcohol screening commonly detects ethanol, the main component of alcoholic beverages. Some screening tests can also identify alcohol consumption through metabolites like Ethyl Glucuronide (EtG) and Ethyl Sulfate (EtS). The presence of these alcohol biomarkers indicates consumption, even if the individual is no longer intoxicated.

Understanding the Results of DAS Screening
The results of DAS screening can have profound implications. Thus, understanding the results of these tests is essential for individuals. Mainly, the screening test results can be classified into three categories: negative, non-negative, or inconclusive. Firstly, a negative result indicates the absence of drugs or alcohol in the system of a person.
Secondly, a non-negative result shows the presence of drugs or alcohol. It means that certain substances have reached the cut-off level to trigger the result. This may require further confirmatory testing to validate the test. It is crucial to note that only laboratory tests can produce a positive result. Also, a non-negative result does not necessarily mean that the individual is impaired at the time of testing.
Thirdly, an inconclusive result means the test is unclear or cannot be interpreted definitively. This may occur due to various factors, such as improper sample collection, handling, or interference from other substances. Lastly, the results from a breathalyser test reflect the current Blood Alcohol Content (BAC) levels of a person.
Implications of a Non-Negative Result
A non-negative result may lead to several implications, depending on the situation or severity. In the workplace, this may result in disciplinary action, up to and including termination of employment. Strict penalties are in place, especially in safety-critical industries, due to the high risk of accidents. Employers can implement these measures by establishing a comprehensive drug and alcohol testing policy.
In roadside screening, the consequences may include on-the-spot fines and licence suspensions. Moreover, in healthcare settings, a non-negative result may lead to further evaluation to diagnose possible substance use disorders. Individuals with addiction may need to undergo treatment and counselling.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DAS screening is a vital process for detecting illegal drug or alcohol use through biological samples. It employs various methods such as urine, saliva, and breath testing, each offering unique advantages in different scenarios. These screenings are accessible through various providers and portable testing kits, delivering rapid results for immediate decision-making. However, the accuracy of results can vary based on testing expertise and methods used. Therefore, confirmatory testing may be necessary to validate non-negative results.
Understanding the results of the screening is crucial, with outcomes falling into three categories: negative, non-negative, or inconclusive. A negative result signifies no drugs or alcohol detected, while non-negative indicates substance presence above the cut-off level. Inconclusive results occur due to various factors, like improper sample handling. Non-negative findings can lead to severe repercussions, such as workplace disciplinary action or license suspension. In healthcare, it prompts further evaluation for substance use disorders.