Breath Test Pathology: Types And Procedure
19 April, 2024

In breath test pathology, health professionals conduct various types of tests. These include urea, hydrogen, methane, and alcohol breath tests. The procedure for these methods typically involves providing a breath sample for analysis. They are valuable tools in diagnosing various medical conditions. Ongoing research and advancements in breath test technology continue to improve their accuracy and broaden their applications. It is important to note that patients have to follow certain preparations to make the test accurate.
What is Breath Test Pathology?
Breath test pathology is a diagnostic tool that helps to identify certain conditions in the body by analysing breath samples. It is useful in detecting disorders such as lactose intolerance and Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO). Through breath testing, doctors can gather information about the functioning of the gastrointestinal system.
In the case of lactose intolerance, the breath test measures the amount of hydrogen in the breath after consuming a lactose-containing beverage. A higher level of hydrogen indicates the inability of the body to properly digest lactose. Similarly, in the case of SIBO, the breath test can detect the presence of gases produced by bacterial overgrowth.
In addition, breath testing has several advantages over traditional blood tests. It is a non-invasive procedure and does not require the extraction of blood samples, making it more comfortable for patients. Moreover, breath testing provides real-time results, making it a quicker and more convenient diagnostic tool. Overall, breath pathology test plays a crucial role in identifying various gastrointestinal disorders, allowing for targeted treatment plans.
Purpose of the Test
- Diagnose a range of medical conditions, including gastrointestinal disorders such as lactose intolerance, fructose intolerance, SIBO, and Helicobacter pylori infection (H. pylori).
- Monitor the effectiveness of treatment for certain conditions. For example, certain breath tests can assess the response to treatment for SIBO by measuring changes in gas production.
- Offer a non-invasive alternative to invasive diagnostic procedures such as endoscopy or blood tests.
- Provide quantitative measurements of specific compounds in the breath, allowing for objective assessment of disease severity or treatment response.
- Detect medical conditions at an early stage, enabling prompt intervention and treatment to prevent complications.

Types of Breath Tests Pathology
Several types of breath tests pathology serve different purposes. Firstly, hydrogen breath testing. In this test, the patient needs to drink a cup of water containing a small amount of fructose, sorbitol, or sucrose. If the patient has a malabsorption issue, their intestinal bacteria will break down the sugar, producing hydrogen gas. The presence of hydrogen in the breath can indicate fructose, sorbitol, or sucrose malabsorption.
Secondly, methane breath testing. This test is similar to hydrogen breath testing, but instead of measuring hydrogen gas, it measures methane gas in the breath. Elevated levels of methane gas in the breath can suggest SIBO. Thirdly, Urea Breath Testing (UBT) detects the presence of H. pylori, a bacteria that can cause stomach ulcers and other gastrointestinal issues.
Lastly, breath alcohol testing. It measures the Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) level of the person. It is a quick and non-invasive way to determine if someone is under the influence of alcohol. In summary, breath tests are a valuable diagnostic tool for a range of conditions. Each test serves a unique purpose in diagnosing various gastrointestinal issues and alcohol consumption.
What Can be Detected?
What can be detected depends on the type of test that people use. For example, hydrogen breath tests can diagnose conditions related to carbohydrate malabsorption, such as lactose intolerance or SIBO. Similarly, methane breath tests detect methane gas production in response to ingested substrates, aiding in the diagnosis of SIBO.
In addition to gastrointestinal disorders, breath tests can also detect bacterial infections and metabolic disorders. The UBT can identify the presence of H. pylori in the stomach. Furthermore, breath alcohol tests, also known as breathalysers, detect the presence of ethanol, a type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages.

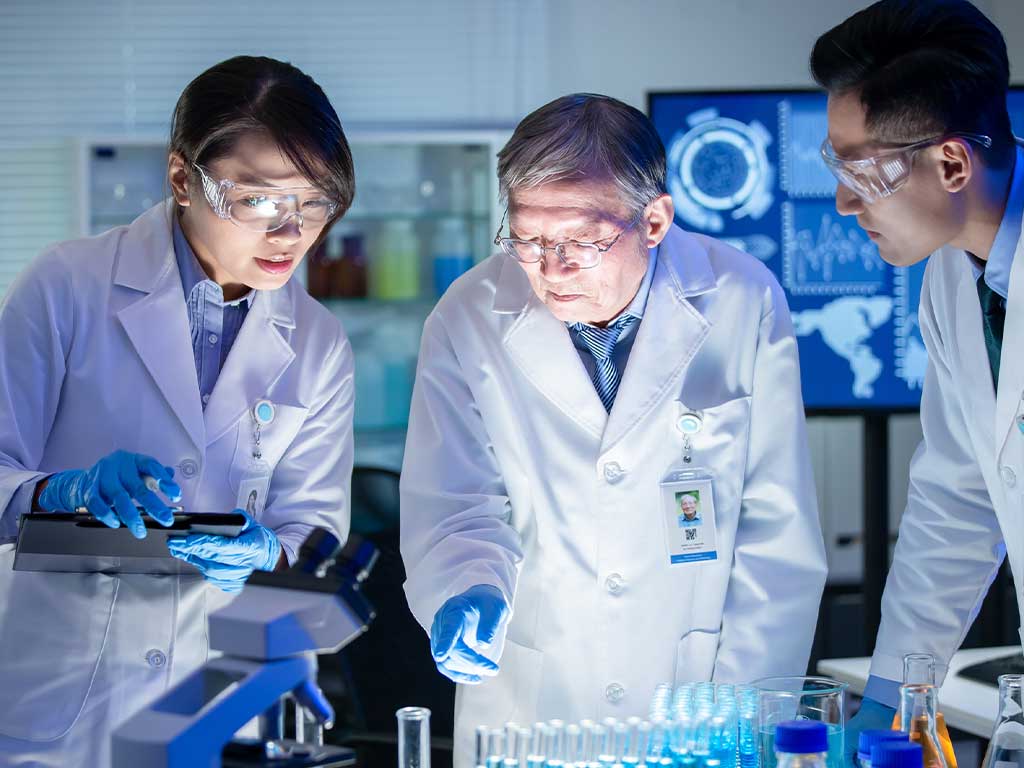
Procedure for Breath Test Pathology
The procedures for breath test pathology also depend on the type of test. In the hydrogen test, the patient drinks a special sugar solution after not eating for a while. Then, the healthcare provider collects breath samples from the patient at different times over a few hours. They check how much hydrogen gas is present, which shows if bacteria in the gut are fermenting carbohydrates.
Similarly, in the methane breath Test, the patient drinks substances that cause gut bacteria to make methane. The medical professional then collects breath samples from the patient and checks them to see how much methane gas is there. This helps them understand if there might be SIBO.
In the UBT, the patient drinks a solution containing labelled urea. If H. pylori bacteria are in the stomach, they use the urea and make labelled carbon dioxide. Healthcare professionals collect breath samples at specific times. If there is labelled carbon dioxide in the breath, it indicates H. pylori infection. For the breath alcohol test, the person blows into the mouthpiece of the breathalyser. The BAC result will be displayed in the LCD after a few seconds.
Preparation for a Breath Test
Preparing for a breath test generally involves adhering to specific instructions to ensure accurate results. These instructions often include refraining from eating, drinking, smoking, or chewing gum for a certain period before the test. This fasting period helps establish a baseline for the composition of the breath.
Additionally, there may be specific guidelines regarding dietary restrictions or medications to avoid before the test. For instance, people might have to avoid certain foods or medications that could potentially interfere with the breath test results. Following these preparation instructions is crucial to obtaining reliable outcomes from the breath test.
Conclusion
Breath test pathology helps doctors identify certain body conditions by analysing breath samples. It is handy for finding problems like lactose intolerance and bacterial overgrowth in the gut. The tests measure gases in breath, showing how well the digestive system works. They are comfortable for patients, giving quick results without invasive procedures. Different tests target specific issues: hydrogen for sugar problems, methane for bacterial overgrowth, urea for stomach bacteria, and alcohol for drunkeness.
The procedures for breath tests vary depending on the type of test. For hydrogen and methane breath tests, patients drink specific solutions, and healthcare providers collect breath samples to analyse gas levels. UBT involves drinking a labelled solution, with breath samples taken to detect H. pylori infection. Breath alcohol testing simply requires blowing into a breathalyser. Preparing for a breath test involves fasting and avoiding certain foods or medications.