Laboratory Test for Alcohol: What It Is & the Types of Tests
12 April, 2024
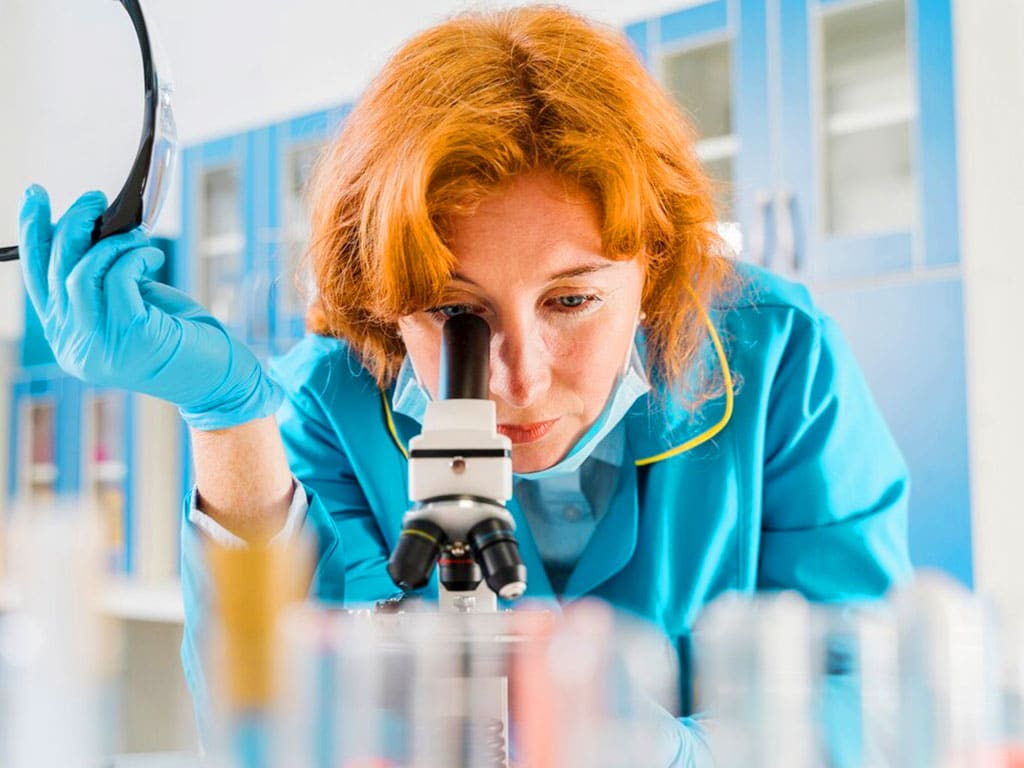

A laboratory test for alcohol is a method used to detect and measure alcohol in a person. It is crucial in various settings, as identification of alcohol use helps prevent accidents or obtain evidence. There are several types of alcohol tests, each with specific processes and sampling procedures. The common methods are breath, urine, blood, and hair tests. Each type is suitable for different occasions or circumstances, such as post-accident, pre-employment, or random testing.
Heavy drinking can have serious repercussions for both the mind and body. It can impair judgment, coordination, and decision-making skills, leading to accidents or injuries. In some cases, excessive alcohol consumption can result in liver damage or alcohol poisoning. Health professionals use lab tests to measure the alcohol levels in the body accurately. The following sections will delve into alcohol laboratory testing, the types of methods available, and the process of conducting the test.
What is a Laboratory Test for Alcohol?
A laboratory test for alcohol is a medical procedure for measuring the Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) level. The test can determine if someone has been drinking and assess their level of intoxication. It is a procedure that is performed in a laboratory or medical facility. Additionally, it requires trained professionals to conduct the test, such as doctors, nurses, phlebotomists, or lab technicians.
Moreover, the procedures involve following strict laboratory standards, chain of custody, and analysis methods to ensure accurate and valid test results. It also undergoes several stages before releasing the final report. This is in comparison with preliminary screening, which can return the results a few minutes after sample collection. Instant test kits and breath-testing devices do not require professionals to administer the test.
Laboratories also perform confirmatory testing to validate the non-negative results of initial screens. It uses advanced techniques like Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) to measure the amounts of alcohol in the sample. Furthermore, a Medical Review Officer (MRO) investigates the samples and finalises the report if a person has indeed consumed alcohol.
Purpose
- Alcohol detection: Determine if a person has consumed alcohol within a certain time frame.
- Legal testing: Provide evidence of alcohol use in cases such as impaired driving, vehicular accidents, workplace accidents, underage drinking, and child custody.
- Confirmation testing: Validates the result of an initial alcohol screening using more advanced analytical methods. An MRO investigates the sample and rules out any potential factors for false positives, such as medical conditions or passive exposure.
- Medical care: Healthcare professionals conduct alcohol tests to diagnose alcohol use disorder and monitor addiction recovery or compliance with prescribed treatments.
- Post-incident testing: Determine whether alcohol is a factor in an accident.

Types of Laboratory Tests for Alcohol
There are different types of laboratory tests for alcohol that can be used for specific situations. The choice of test depends on various factors such as the purpose, detection window, and level of accuracy. The first type is the breath alcohol test. It is a non-invasive method of detecting alcohol using a breathalyser. The device measures the BAC through the sample of breath.
Another common method is the urine test. This test can trace direct biomarkers of ethanol, such as Ethyl glucuronide (EtG) and Ethyl sulfate (EtS). These are metabolites that the body produces after consuming alcohol. They can stay in urine for 48-72 hours after intake. However, it is important to note that the presence of these alcohol biomarkers does not necessarily entail current impairment or intoxication.
In addition, blood tests offer the highest accuracy in measuring alcohol levels. It involves a phlebotomist or trained professional to draw a blood sample. Lastly, the hair follicle test can trace alcohol metabolites for up to 90 days. This can provide a comprehensive history or patterns of alcohol use.
Steps Involved in Collecting Samples
Collecting biological samples involves several steps to ensure accurate and reliable results. The first step is to use sterile or new testing devices or equipment. Additionally, some tests require specified minutes or hours before providing a sample. For a breath test, a person blows into a breathalyser device.
For urine testing, the person must fill a small container cup to a specific amount. Meanwhile, blood sampling involves using a needle to puncture the vein and then suction it into a tube. Lastly, for hair testing, a collector cuts a small sample of hair and sends it to the laboratory for analysis.

Process of Laboratory Test for Alcohol
Laboratory tests for alcohol follow standard procedures to ensure accuracy. The process typically involves sample collection, chain of custody, analysis, and interpretation of results. Firstly, administrators facilitate sample collection. They must ensure that the testing environment is clean and free from any contaminants. Secondly, ensure chain of custody procedures. It involves proper labelling, handling, and storage of the specimens to prevent adulteration or tampering.
Thirdly, analysis is the most crucial aspect of alcohol testing. The sample undergoes laboratory analysis to measure the precise level of alcohol. Different laboratories use various techniques, such as GC-MS or enzymatic assays. Depending on the type, the results may be available after a few hours or days.
Lastly, the laboratory generates a report indicating the results of the test. It includes the blood alcohol concentration levels, and any applicable reference ranges for interpretation. The presence of alcohol results in a positive test. Furthermore, if the blood alcohol levels are high, it may indicate recent heavy drinking. Trained professionals interpret the results based on specific criteria for alcohol use.
Implications of Exceeding the Legal Limit
Exceeding the legal limit of alcohol can have legal implications. In many jurisdictions, driving with a BAC level of 0.05% or higher is illegal and can result in penalties such as fines, licence suspension, or even imprisonment. Police officers conduct roadside breath tests to detect drivers who exceed the legal limit.
Some workplaces implement zero tolerance to alcohol policy. Violation of this policy may lead to disciplinary actions or termination of employment. Moreover, it can help determine the drinking habits of a person or if they have chronic alcohol abuse issues. This may necessitate intervention for treatment or counselling to address the underlying issues.
Conclusion
Laboratory tests for alcohol play a crucial role in measuring alcohol levels in the body. These tests aim to detect alcohol impairment, which may pose safety risks or hazards. In addition, it can help determine if a person has alcohol dependence problems. Laboratories use different methods, such as breath, urine, hair, and blood alcohol tests. Nevertheless, following strict protocols in sample collection and analysis is essential to ensure the accuracy of the test.
Medical facilities interpret the test results based on specific criteria to provide reliable information. Positive tests can have several implications. For instance, exceeding the legal alcohol limit may result in fines and court proceedings. Employees may also face disciplinary actions. Alcohol testing can also help determine if a person has harmful alcohol consumption habits that may need intervention. Overall, laboratory tests are valuable for identifying alcohol-related issues and promoting safety and well-being.