Drug and Alcohol Testing in the Workplace Australia: The Need to Know
30 April, 2024

Drug and alcohol testing in the workplace in Australia is a crucial practice where employers check their employees for illicit substances. There are various methods to conduct this test, like urine, saliva, blood, hair, and breath tests. In addition, workplaces implement these testing programs during pre-employment, random, blanket, and post-accident cases, among others. Workplace testing is supported by key legislations that mandate employers to provide a safe work environment.
Drug and alcohol abuse can result in various detrimental effects. In the short term, it can lead to impairment, which can increase the likelihood of accidents and injuries. Over time, it may lead to health issues and reduced productivity. By implementing workplace policies, employers can take appropriate action to ensure workplace safety. This comprehensive guide will provide more information about workplace drugs and alcohol testing, including its types and legal framework.
Overview of Drug and Alcohol Testing in the Workplace in Australia
Drug and alcohol testing in the workplace in Australia is a practice where employers check their current or prospective employees for illicit substance use. It can detect illegal drugs, prescription drugs, and alcohol. Accordingly, employers across various sectors conduct these tests. These procedures are particularly prevalent in safety-critical industries, such as the mining industry, heavy vehicle operators, and rail transport operators.
The testing procedure begins by creating a clear testing policy. Then, employers inform employees or job applicants about the policy and may need to give consent. Subsequently, employers notify individuals when they are selected for testing. It can be for pre-employment testing, random testing, reasonable suspicion testing, post-accident testing, or blanket testing.
Furthermore, a trained professional performs sample collection. It could be urine, oral fluid, blood, hair, or breath samples. The specimens are tested for drugs, alcohol, or both, depending on the company policy. Organisations have the option to conduct onsite testing or send samples to a laboratory. Finally, employers receive the test results and may take appropriate action accordingly.
Importance of Workplace Testing
- Enhances workplace safety: Testing helps ensure that employees are not under the influence of alcohol or illicit drugs that could impair their ability to work safely.
- Boosts workplace productivity: Testing regime promotes a culture of sobriety that is conducive to maximising productivity.
- Improves occupational health: It encourages employees to lead healthier lives, which can result in lower healthcare costs for employers.
- Maintain reputation: Companies can demonstrate their commitment to a professional and responsible business environment.
- Ensures legal compliance: Companies must comply with relevant standards or industry regulations. The testing helps avoid penalties, lawsuits, or loss of operational licences.
Types of Drug and Alcohol Testing in the Workplace in Australia
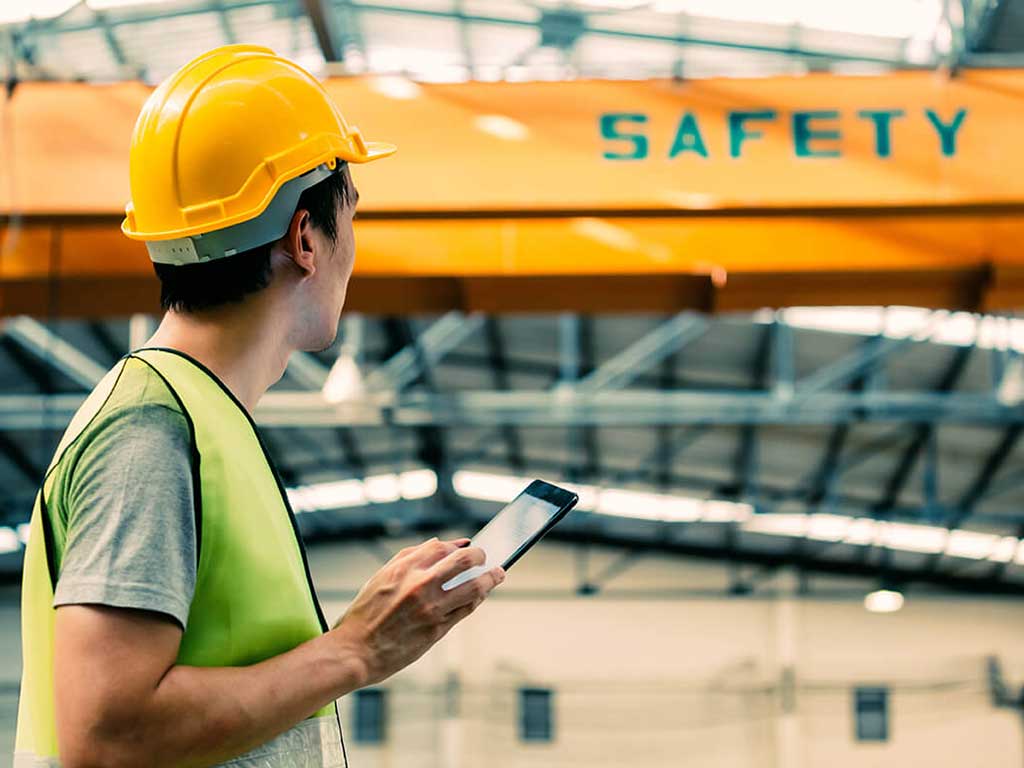
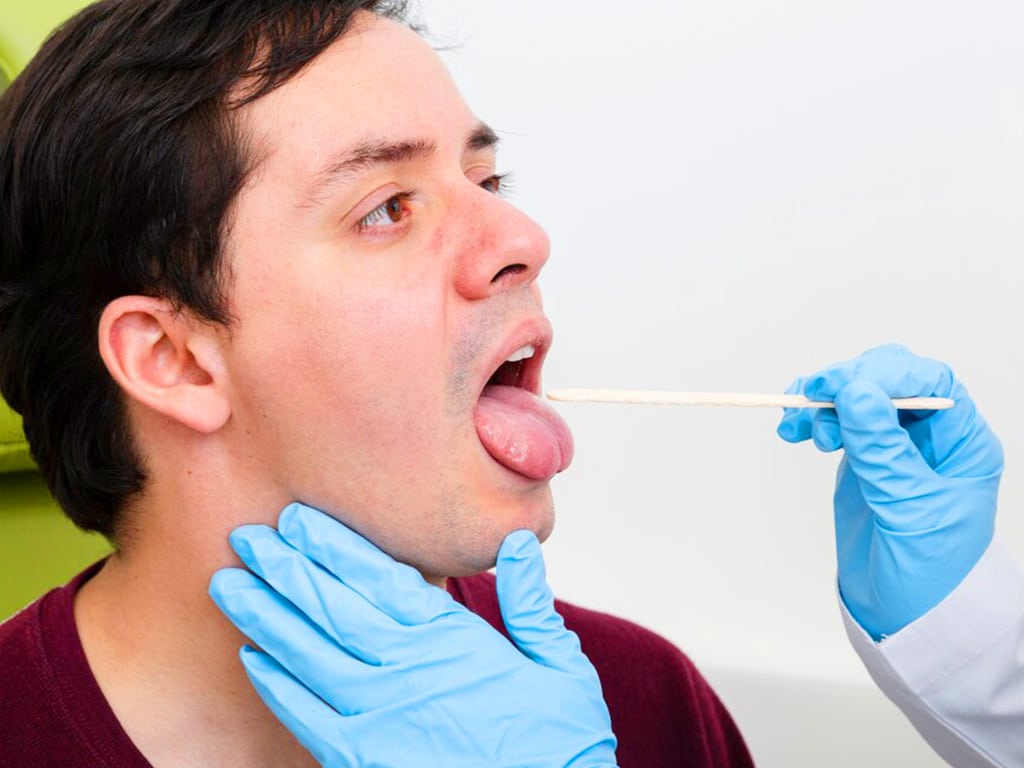
There are various types of drug and alcohol testing in the workplace in Australia. Each type has its advantages and limitations. Firstly, urine test. This process is easy and convenient. Urine tests can identify and trace a wide range of substances in urine samples for up to three days to one week. It is also easy to administer and provides quick results.
Secondly, saliva test. It is a non-invasive process that involves swabbing the inside of the mouth to obtain saliva samples. The test is also quick and can determine recent drug and alcohol consumption. Thirdly, breath test. It involves blowing into a breathalyser device to measure Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) levels.
Fourthly, blood test. It provides highly accurate and detailed information regarding alcohol and drug levels in the blood sample. However, it is less common because it can be invasive, costly, and time-consuming. Lastly, hair follicle test. It can detect long-term drug and alcohol use. It can trace drug metabolites in hair samples for up to 90 days before the test date.
Substances that Can be Detected
Workplace testing can detect various substances. Foremost, it can monitor the presence of illicit drugs. These include cannabis, cocaine, heroin, ecstasy, and methamphetamine, all of which impair cognitive and physical abilities. Additionally, workplace testing can detect ethanol, the main active ingredient in alcoholic beverages.
Prescription medications also fall under scrutiny. These are pharmaceutical drugs prescribed by professionals to typically treat severe medical conditions, including opiates, opioids, amphetamines, and benzodiazepines. Despite their legality, misusing these drugs remains prohibited. Overall, these are the substances that employers often screen for to ensure a safe and productive work environment.

Legal Framework for Drug and Alcohol Testing in the Workplace in Australia
The legal framework for drug and alcohol testing in the workplace in Australia is founded on several key pieces of legislation. Foremost, the Fair Work Act 2009 governs the employer-employee relationship. Under this act, employers are tasked with providing a safe work environment, which implicitly includes managing the influence of alcohol and drugs. Additionally, the act protects employees from unfair treatment.
Moreover, the Work Health and Safety Act requires employers to manage health and safety risks in the workplace proactively. It includes preventing accidents and injuries that could result from drug or alcohol impairment. This law encourages employers to identify potential risks related to substance use and to implement a variety of control measures.
Furthermore, Australian laws mandate that these policies respect individual privacy. Employers must handle the testing process and results confidentially. Thus, they must only share information with those who need or are authorised to know. Transparency is also crucial to maintain trust. Employers often develop policies within this legal framework.
Can an Employee Refuse a Test?
Workplace drug and alcohol testing can be a sensitive issue for some people. While it may be mandatory for some organisations, some employees may feel uncomfortable or hesitant about undergoing such tests. In most cases, employees cannot refuse to participate in a workplace drug and alcohol testing procedure without facing consequences.
Refusing to undergo workplace testing could result in disciplinary or legal actions, including termination. It is especially critical if the employee accepts the terms in the initial employment agreement. However, there may be instances where employees may refuse a test for valid reasons. It includes certain medical conditions or improper testing procedures.
Conclusion
Drug and alcohol testing in the workplace in Australia is a vital practice to ensure a safe and productive work environment. Various testing methods, such as urine, saliva, breath, blood, and hair follicle tests, can detect substance use among employees. Each method offers different advantages and limitations depending on the situation. However, companies must have clear testing policies in place and conduct testing responsibly to avoid any legal issues or privacy concerns.
The legal framework for workplace testing is essential. Employers must comply with laws such as the Fair Work Act 2009 and the Work Health and Safety Act to protect employees from harm and promote workplace safety. By implementing policies that respect individual privacy and confidentiality, employers can create a safe and supportive work environment while also ensuring compliance with legal requirements. Transparency is also crucial for maintaining trust between employers and employees.